BLE Beacon
Materials
AMB82-mini x 1
Android / iOS mobile phone
Example
Introduction
A BLE beacon broadcasts its identity to nearby Bluetooth devices, to enable the other devices to determine their location relative to the beacon, and to perform actions based on information broadcasted by the beacon.
Example applications of beacons include indoor positioning system, location-based advertising and more.
From the definition of its purpose as a broadcast device, a BLE beacon thus cannot be connected to, and can only send information in its Bluetooth advertisement packets.
There are several BLE beacon protocols. The Ameba BLEBeacon library supports the iBeacon and AltBeacon protocols.
Procedure
Ensure that the following Bluetooth apps are installed on your mobile phone. These apps will show you the raw data sent by Ameba and allow you to interact with the data.
The recommended application is nRF connect, and is available at the links below:
Android: https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=no.nordicsemi.android.mcp
iOS : https://apps.apple.com/us/app/nrf-connect/id1054362403
LightBlue is an alternative application that can also be used, but has less features:
Open the example, “Files” -> “Examples” -> “AmebaBLE” -> “BLEBeacon”
Upload the code and press the reset button on Ameba once the upload is finished.
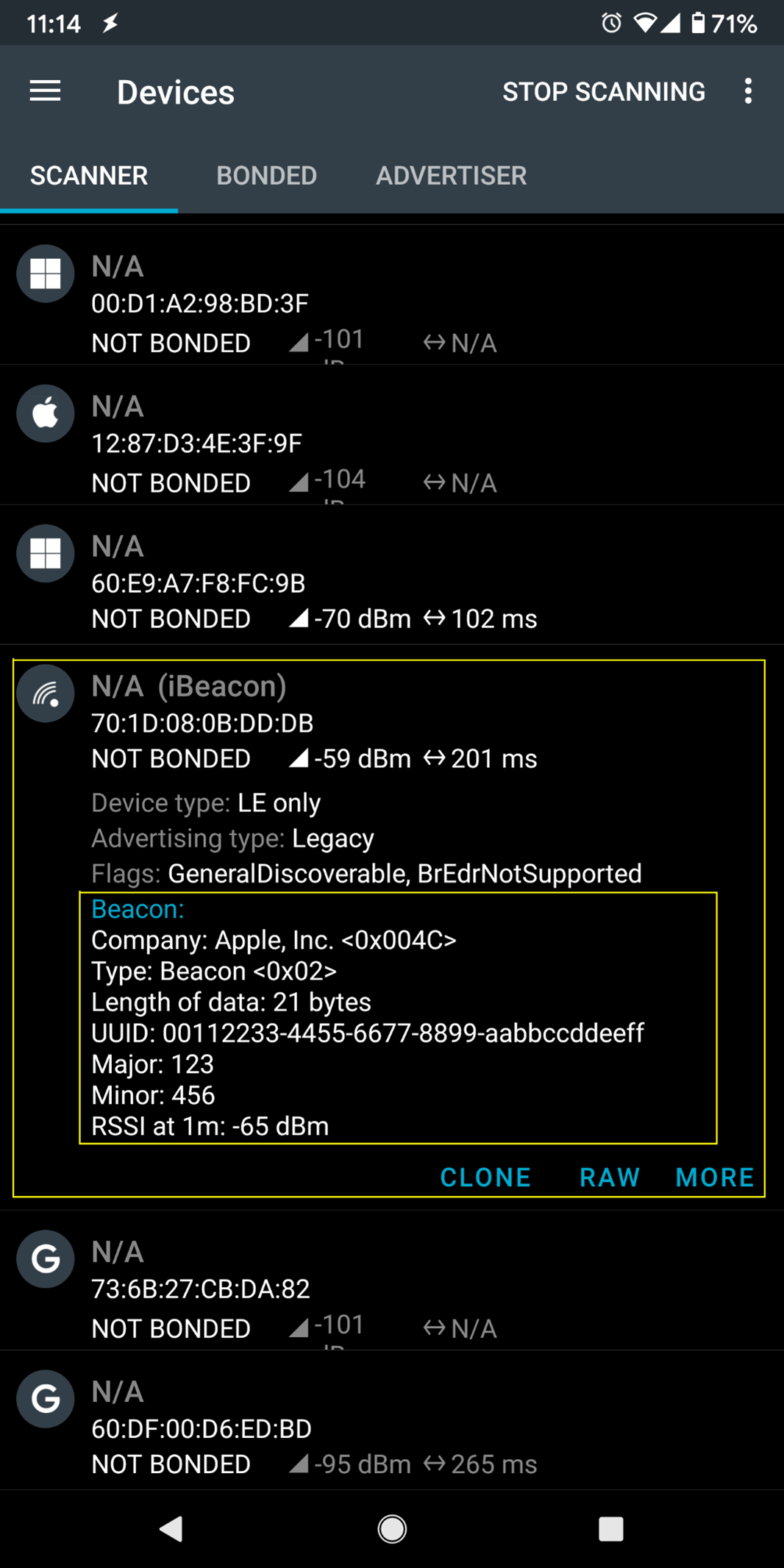
On your mobile phone, open the Bluetooth app and scan for the beacon signal broadcast by Ameba.
If you happen to be in an environment with multiple BLE beacons, you can tap the entries to expand them, and verify that the beacon data is identical to the data in the sketch.
Code Reference
setRssi() is used to set the received signal strength indicator (rssi)
data field for a beacon. The specification states that this should be
the received signal strength from the beacon at a 1 meter distance.
With no method to measure this, it is set to -65dBm as an estimate.
setMajor() and setMinor() are used to set the two data fields. The
purpose of these data are left for the manufacturer of the beacon to
define, and can be used in any way.
setUUID() is used to give the beacon a universally unique identifier
(UUID). This is a 128-bit number usually expressed as a hexadecimal
string. It is used to identify each unique beacon, and can be randomly
generated for free online.
The BLEBeacon library includes both iBeacon and AltBeacon classes,
replace line 6 iBeacon with altBeacon to create an AltBeacon instead.
The data fields are mostly the same, with only minor changes, please
look at the header files for more details.
BLE.init() is used to allocate memory and prepare Ameba for starting
the Bluetooth stack.
BLE.configAdvert() is used to configure the Bluetooth advertisement
settings, to which we pass the beacon data and set the device as
non-connectable.
BLE.beginPeripheral() starts Ameba in Bluetooth peripheral mode, after
which it will begin to advertise with the beacon data provided.