Set up MQTT Client to Communicate with Broker
Materials
AMB82-mini x 1
Example
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is a protocol proposed by IBM and Eurotech. The introduction in MQTT Official Website: MQTT is a machine-to-machine (M2M)/”Internet of Things” connectivity protocol. It was designed as an extremely lightweight publish/subscribe messaging transport.We can say MQTT is a protocol designed for IoT. MQTT is based on TCP/IP and transmits/receives data via publish/subscribe.
Please refer to the figure below:
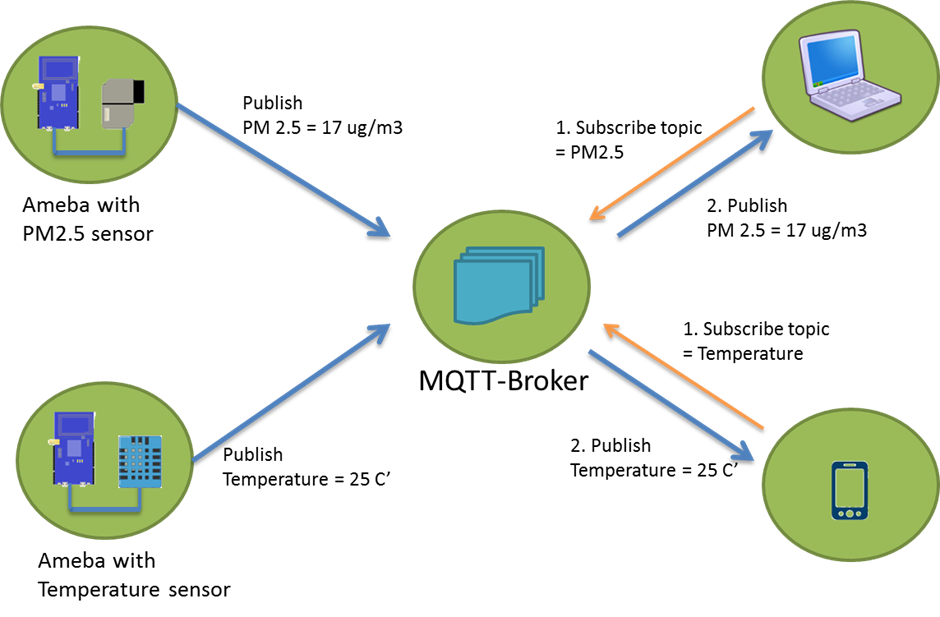
In the operation of MQTT, there are several roles:
Publisher: Usually publishers are the devices equipped with sensors (ex. Ameba). Publishers uploads the data of the sensors to MQTT-Broker, which serves as a database with MQTT service.
Subscriber: Subscribers are referred to the devices which receive and observe messages, such as a laptop or a mobile phone.
Topic: Topic is used to categorize the messages, for example the topic of a message can be “PM2.5” or “Temperature”. Subscribers can choose messages of which topics they want to receive.
In this page, there are 3 examples that connect Ameba to MQTT-Broker. Then send messages as publisher and receive messages from MQTT-Broker as subscriber.
MQTT_Basic
MQTT_Auth
MQTT_Publish_In_Callback
MQTT_Basic example
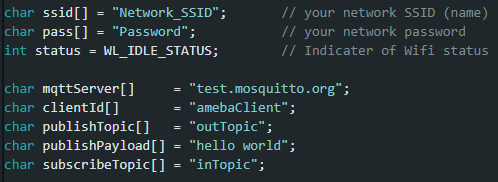
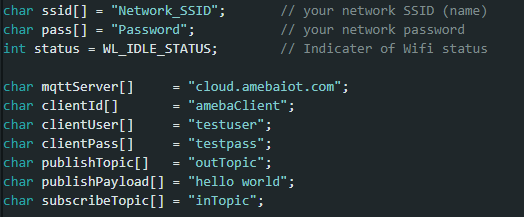
“ssid” is the network SSID for internet access.
“pass” is the network password for internet access.
“mqttServer” refers to the MQTT-Broker, there is free MQTT sandbox “test.mosquitto.org” for testing.
“clientId” is an identifier for MQTT-Broker to identify the connected device.
“publishTopic” is the topic of the published message in the example it is “outTopic”. The devices that subscribed to “outTopic” will receive the message.
“publishPayload” is the content to be published.
“subscribeTopic” is to tell MQTT-broker which topic to subscribe to by the board.
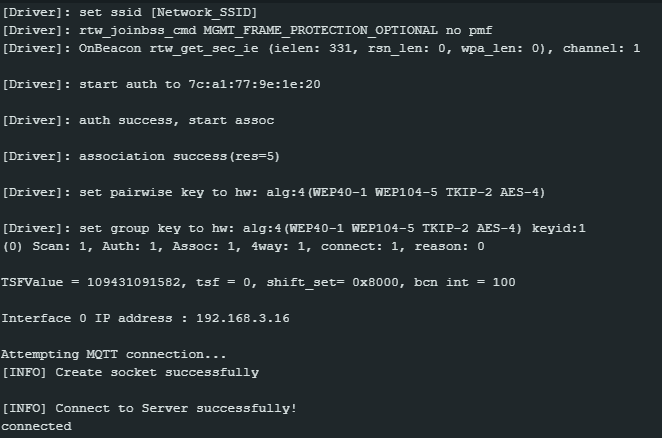
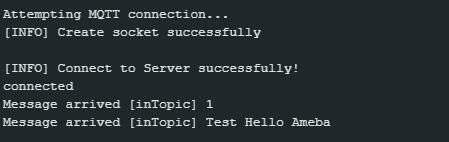
Next, compile the code and upload it to Ameba. Press the reset button, then open the serial monitor.
After Ameba is connected to MQTT server, it sends the message “hello world” to “outTopic”. To see the message, another MQTT client needs to be set up.
The “MQTT Explore” is an all-platform application that can be set as the MQTT client. Refer to the website http://mqtt-explorer.com/.
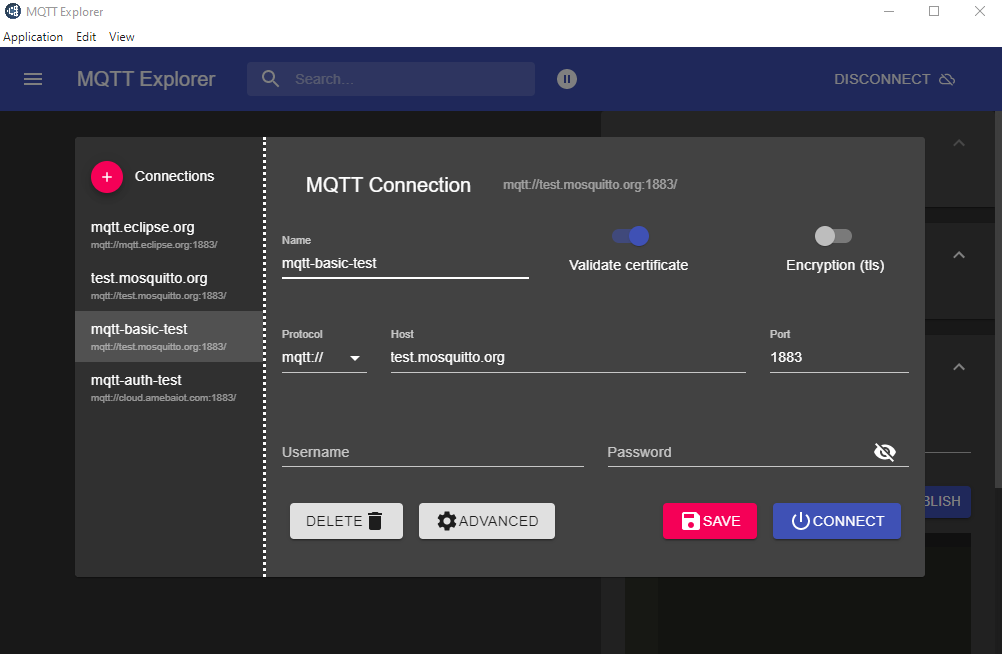
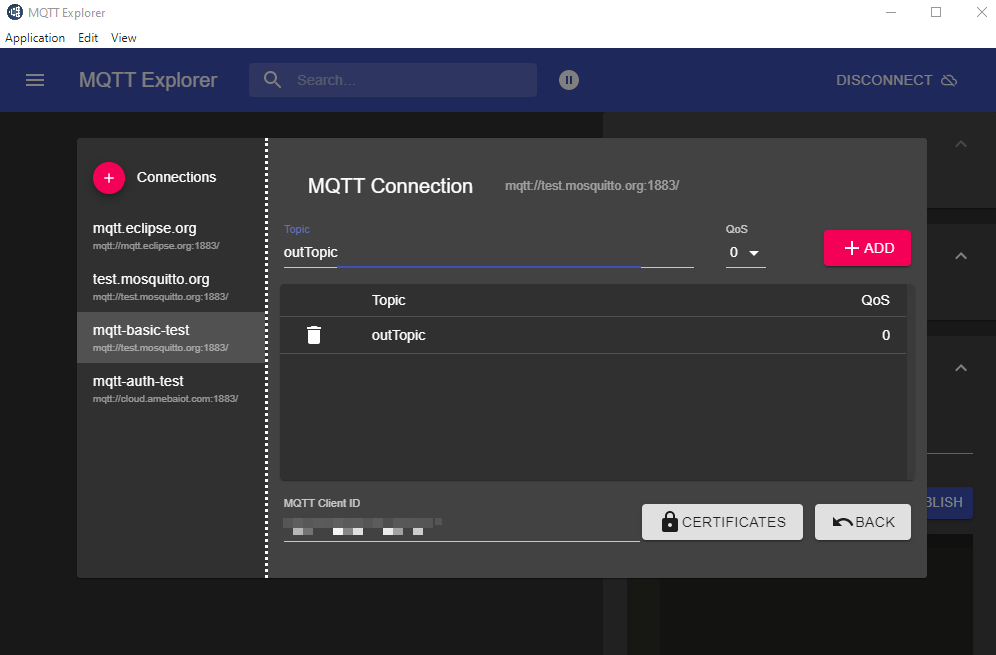
Click “Connections” at top left to start a new connection setup. “Name” can be customized. Set “Host” as “test.mosquitto.org”.
Click “ADVANCED” at bottom for topic setup. Use “outTopic” that same as “publishTopic” of the board. Click “ADD” then “BACK”.
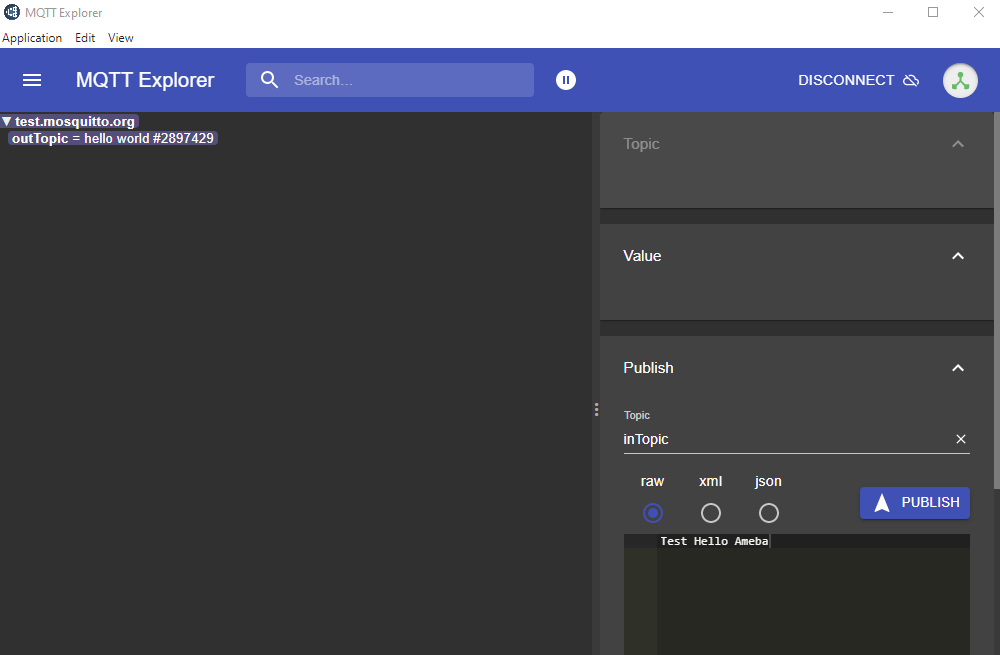
Click “CONNECT”. The “hello world” message show up at left side. At right side, under “Publish” use “inTopic” same as “sucribeTopic” of the board. Choose “raw” and input “Text hello Ameba”, then click “PUBLISH”. The board will receive the MQTT Explorer published raw message. Note, because of the host is a free public host, the board may receive unexpected messages.
MQTT_Auth example
“mqttServer” refers to the MQTT-Broker, there is free MQTT auth host provided by amebaiot homepage “cloud.amebaiot.com”. Please visit https://www.amebaiot.com/en/cloud-getting-started/ for account setup.
“clientId” is an identifier for MQTT-Broker to identify the connected device. In this case, it is the registered device name. Refer to https://www.amebaiot.com/en/cloud-service/.
“clientUser” is the authentication username. In this case, it is the login username of Realtek IoT/Wi-Fi MCU Solutions website. Note, it will be unable to receive message if use the email as “clientUser”.
“clientPass” is the authentication password. In this case, it is the login password of Realtek IoT/Wi-Fi MCU Solutions website.
The other parameters are same as pervious.
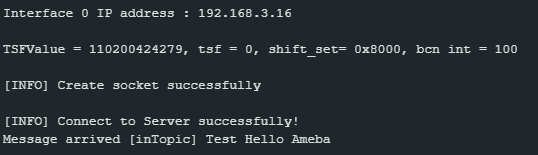
Next, compile the code and upload it to Ameba. Press the reset button, then open the serial monitor. After Ameba is connected to MQTT server, it sends the message “hello world” to “outTopic”. To see the message, another MQTT client needs to be set up.
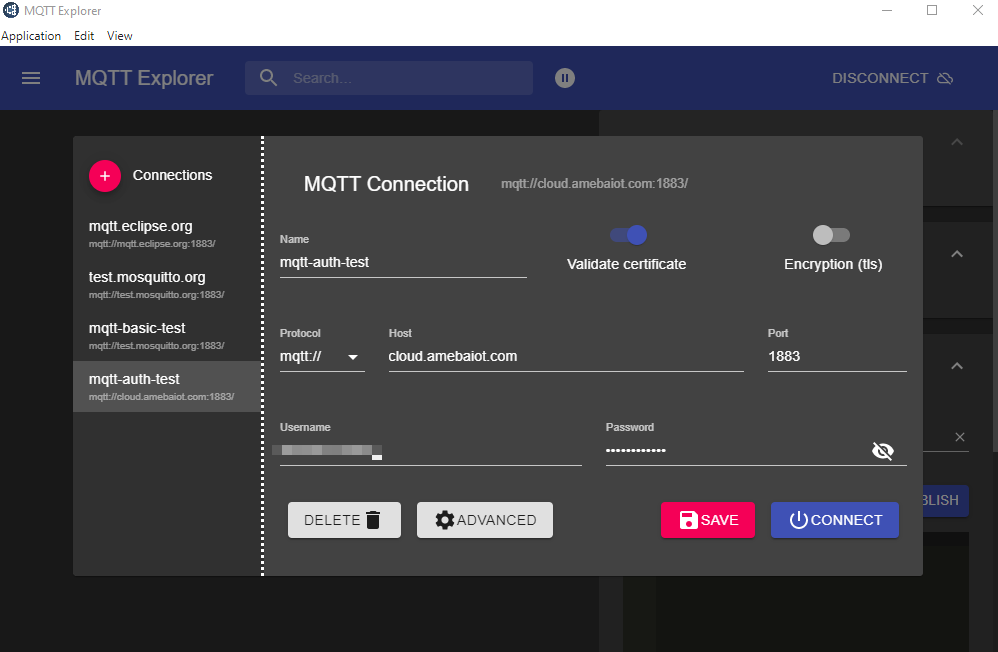
Start the MQTT Explore, and setup the auth connection.
Click “Connections” at top left to start a new connection setup. “Name” can be customized. Set “Host” as “cloud.amebaiot.com”. “Username” and “Password” are same as “clientUser” and “clientPass”.
Click “ADVANCED” at bottom for topic setup. Use “outTopic” that same as “publishTopic” of the board. Click “ADD” then “BACK”.
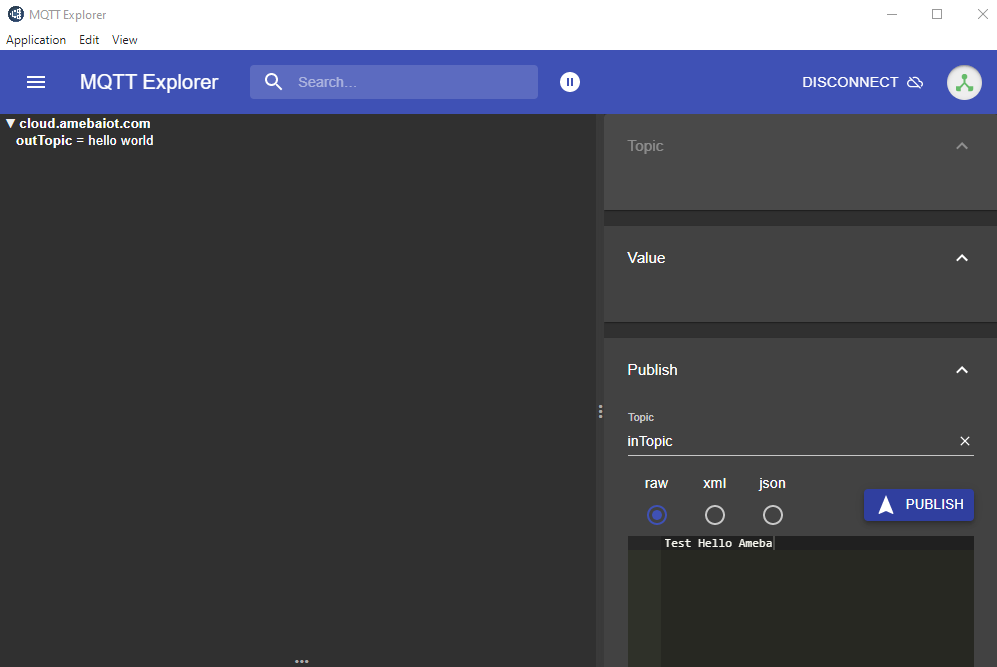
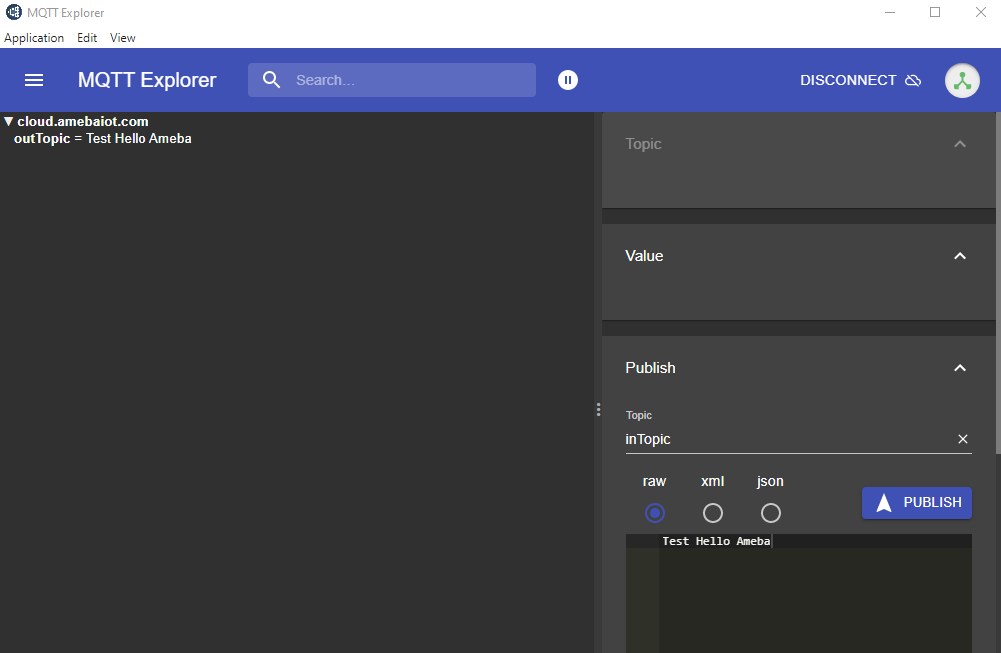
Click “CONNECT”. The “hello world” message show up at left side. At right side, under “Publish” use “inTopic” same as “sucribeTopic” of the board. Choose “raw” and input “Text hello Ameba”, then click “PUBLISH”. The board will receive the MQTT Explorer published raw message. Note, “hello world” sometimes is not shown up because the boards connect to MQTT broker before the MQTT Explorer.
MQTT_Publish_In_Callback example
Open the MQTT example “File” -> “Examples” -> “AmebaMQTTClient” -> “MQTT_Publish_In_Callback”
Please modify some WiFi-related parameter and some information related to MQTT:
All parameters are same as MQTT_Auth example.
Next, compile the code and upload it to Ameba. Press the reset button, then open the serial monitor. After Ameba is connected to MQTT server, it sends the message “hello world” to “outTopic”. To see the message, another MQTT client needs to be set up.
Start the MQTT Explore, and setup the auth connection. All setting is same as MQTT_Auth example.
Click “ADVANCED” at bottom for topic setup. Use “outTopic” that same as “publishTopic” of the board. Click “ADD” then “BACK”.
Click “CONNECT”. The “hello world” message show up at left side. At right side, under “Publish” use “inTopic” same as “sucribeTopic” of the board. Choose “raw” and input “Text hello Ameba”, then click “PUBLISH”. The board will receive the MQTT Explorer published raw message. Then publish it from the board side and MQTT Explorer will receive at the left side. Note, “hello world” sometimes is not shown up because the boards connect to MQTT broker before the MQTT Explorer.