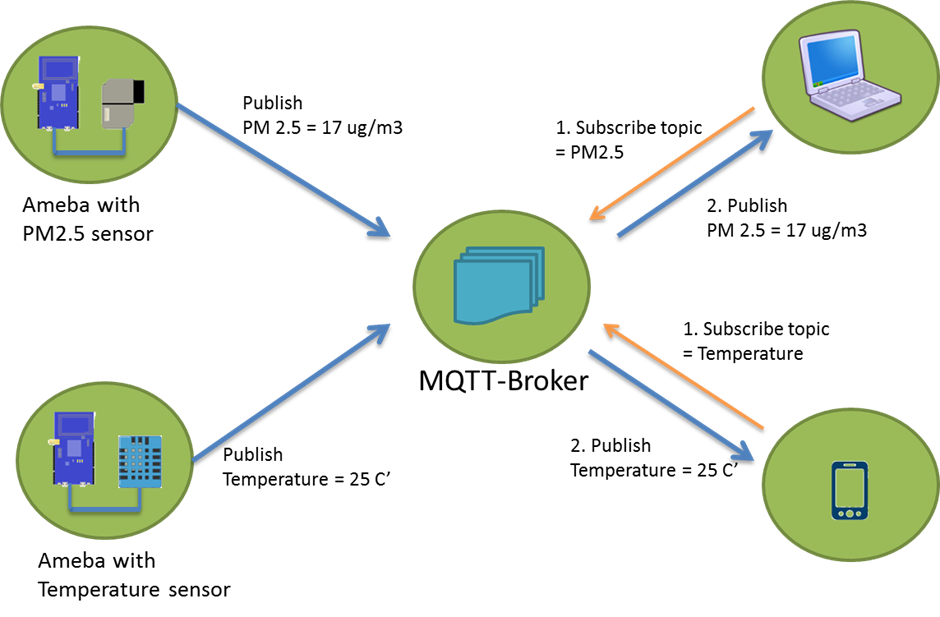
Master Receive Data from Arduino UNO
Materials
AMB82-mini x 1
Arduino UNO x 1
Example
I2C Introduction
There are two roles in the operation of I2C, one is “master”, the other is “slave”. Only one master is allowed and can be connected to many slaves. Each slave has its unique address, which is used in the communication between master and the slave. I2C uses two pins, one is for data transmission (SDA), the other is for the clock (SCL). Master uses the SCL to inform slave of the upcoming data transmission, and the data is transmitted through SDA. The I2C example was named “Wire” in the Arduino example.
Introduction
In the example “I2C - Send Data to Arduino Uno”, Ameba, the I2C master, transmits data to the Arduino UNO, the I2C slave. As to this example, Ameba is the I2C master, and receives data from the Arduino UNO, which is the I2C slave.
Procedure
Setting up Arduino Uno to be I2C Slave
Then click “Sketch” -> “Upload” to compile and upload the example to Arduino Uno.
Setting up Ameba to be I2C Master
Click “Sketch” -> “Upload” to compile and upload the example to Ameba.
Wiring
AMB82 MINI wiring diagram:
Code Reference
Wire.begin() / Wire.begin(address) to join the I2C bus as a master or slave, in the Master case the address is not required.Wire.requestFrom() to specify from which Slave to request data.