Simple TCP Server
Materials
AMB82-mini x 1
Laptop (Make sure it is connected to the same network domain as Ameba, and TCP tools are installed.)
Example
In this example, we first connect Ameba to WiFi, then we use Ameba as server to communicate with client.
First, we make sure the correct Ameba development board is set in “Tools” -> “Board”
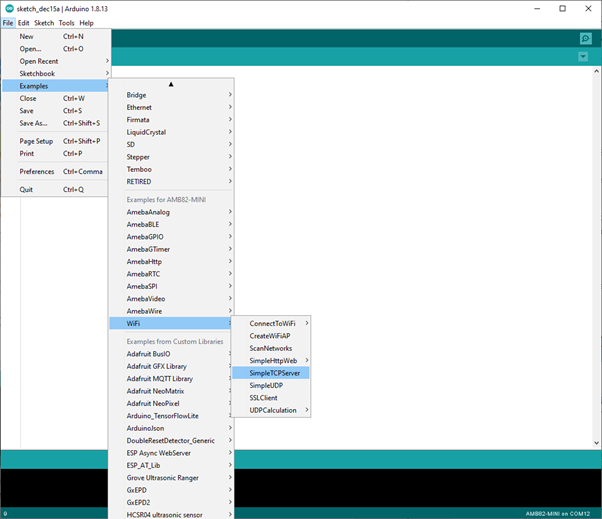
Then, open the Simple WiFi Server example in “File” -> “Examples” -> “WiFi” -> “SimpleTCPServer”:
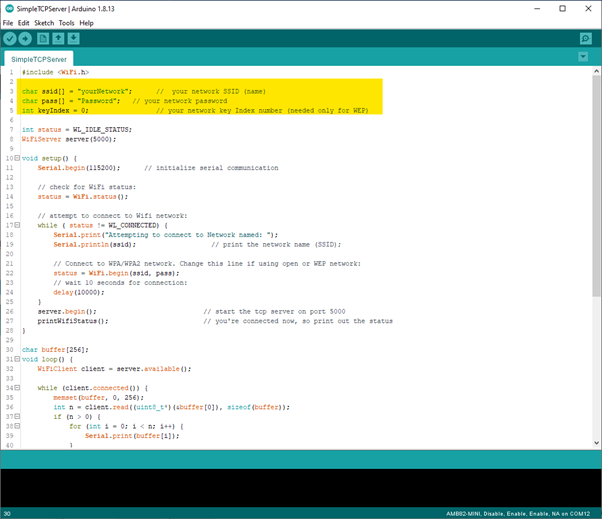
In the sample code, modify the highlighted parameters and enter the ssid and password for your WiFi connection.
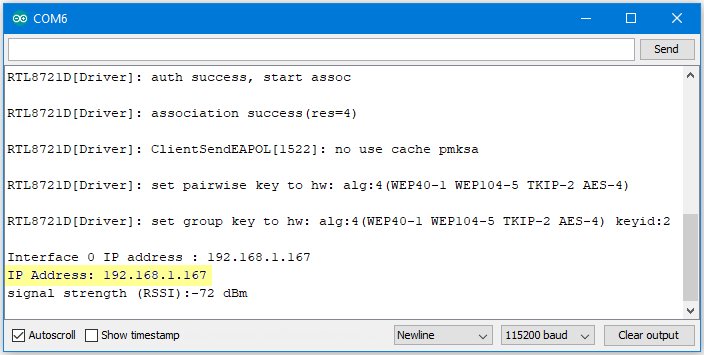
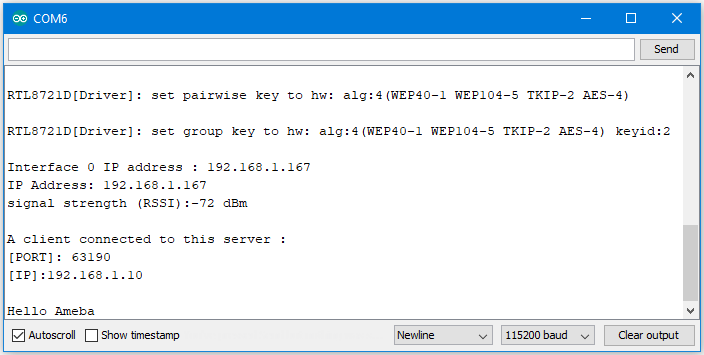
Next, upload the code, then press the reset button on Ameba. Afterwards, you will see the connection information is displayed in the serial monitor.
Next, we use the socket tool in the laptop to be the client and connect to the IP address of the Ameba board shown in the connection information at port 5000. (Note: The socket tool we used in this example is “sokit”)
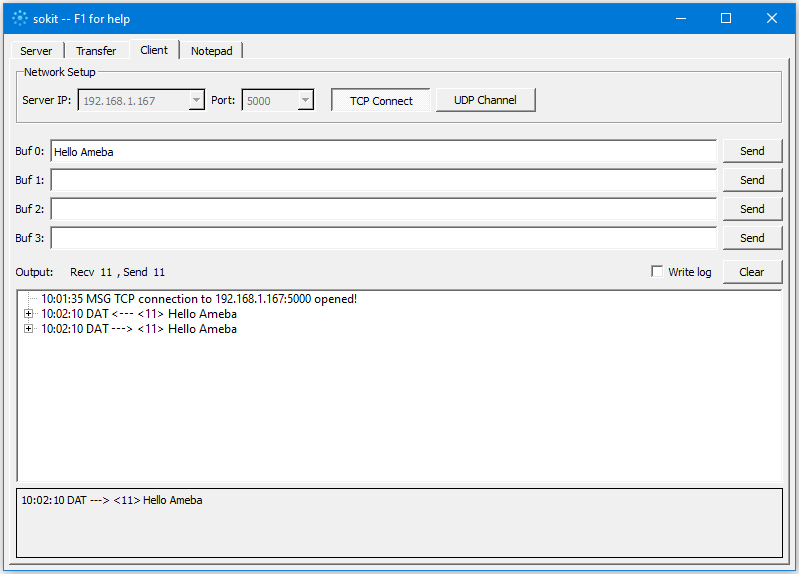
Click on the “Client” tab to choose the client mode, specify the IP and port of the server, then click “TCP Connect”.
If the connection is established successfully, the server shows a message: “A client connected to this Server”, and the IP and port of the connected client.
In this example, when the client and server are connected and the client sends a string to Ameba server, the Ameba server returns the identical string back to the client.
The string sent to server is returned and showed at the client side.
Code reference
WiFi.begin() to establish WiFi connection;WiFi.SSID() to get SSID of the current connected network.WiFi.RSSI() to get the signal strength of the connection.WiFi.localIP() to get the Ameba WiFi shield’s IP address.Server(port) to create a server that listens on the specified
port.server.begin() to tell the server to begin listening for incoming
connections.server.available() to get a client that is connected to the server
and has data available for reading.client.read() to read the next byte received from the server.client.write() to write data to the server.client.stop() to disconnect from the server.